Keywords: Keywords: W. Lyman, et l, AIDS, Electric Current, lymphoblastoid
cell lines (H9 and CEM-SS), HIV-1, AIDS, tritiated thymidine (3H-TdR), HBWSS,
Syncytium-formation assay, varicella, The RF Strain, (SDH), H+(ATP).
see also :
http://www.rexresearch.com/kaali/kaali.htm
CLICKHERE
OR HERE
http://educate-yourself.org/be/
CLICKHERE
OR HERE
US Patent # 5,185,086 Kaali , et al.
February 9, 1993
Method and system for treatment of blood
and/or other body fluids and/or synthetic fluids using combined filter
elements and electric field forces
US Patent # 5,188,738
Kaali , et al. February 23, 1993
Alternating current supplied
electrically conductive method and system for treatment of blood and/or
other body fluids and/or synthetic fluids with electric forces
US Patent # 5,139,684
Kaali , et al. August 18, 1992
Electrically conductive
methods and systems for treatment of blood and other body fluids and/or
synthetic fluids with electric forces
US Patent # 5,817,142
Corder October 6, 1998
Electrical apparatus for killing micro-organisms in the human body
US Patent #
6,539,252 Fields , et al. March 25, 2003
Method and apparatus for the treatment of blood
borne pathogens such as immunodeficiency virus
US Patent #
5,352,192 Byrne , et
al. October 4, 1994
Medical device
================================================================================
VIDEO
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l_z9FQxfeT0
IS
NO LONGER AVAILABLE IN
"YOU
TUBE"
.....CLICKHERE
For the saved page from
youtube
CLICKHERE
For the saved page's title from google
CLICKHERE
SOME STATISTICAL DATA FOR THIS VIDEO EXIST IN
"YOU TOMB" : http://youtomb.mit.edu/youtube/l_z9FQxfeT0
clickhere
CLICK HERE
FOR THE SAVED WEBPAGE FROM "YOU
TOMB"
Below follow three ''YOU TUBE" videos with the same theme
........
================================================================================
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XAXCwFJVeuA
v=XAXCwFJVeuA for the saved webpage click here
http://www.youtube.com/comment_servlet?all_comments&v=XAXCwFJVeuA&fromurl=/watch%3Fv%3DXAXCwFJVeuA
saved webpage with
All Comments (162 total)
================================================================================
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V1otPs4slq0
v=V1otPs4slq0 for
the saved webpage click here
http://www.youtube.com/comment_servlet?all_comments&v=V1otPs4slq0&fromurl=/watch%3Fv%3DV1otPs4slq0
saved webpage with
All Comments (239 total)
click here
================================================================================
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kZ4nOCJsbQo
v=V1otPs4slq0
for the saved webpage click here
http://www.youtube.com/comment_servlet?all_comments&v=kZ4nOCJsbQo&fromurl=/watch%3Fv%3DkZ4nOCJsbQo%26feature%3Drelated
saved webpage with All Comments ( 37 total)
click here
================================================================================
see also :
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-234247273689402090&hl=en
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=2095786730805958061&hl=en
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-3383948315844437935&hl=en
================================================================================
http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/microelectricitygermkiller/
http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/Beck-n-stuff/
http://bioelectricbuzz.tribe.net/thread/56c3a283-a83c-43ae-a80b-d71704ba5aae
http://www.in-my-opinion.org/in-my-opinion-5016.html&sid=0449e90f9ec8b93aacb5408932db8a9f
http://community.freespeech.org/blood_electrification_suppressed
http://www.ehealthforum.com/health/topic28850.html
http://curezone.com/forums/am.asp?i=59058
http://www.epanorama.net/wwwboard/messages/8852.html
......... Back in 1995
in a 73 magazine editorial I explained about Drs. Lyman and Kaali at the
Albert Einstein College of Medicine at Yeshiva University in New York City
serendipitously discovering that when a tiny electrical current was passed
through the blood it prevented any virus, germs, or parasites trying to live
in the blood from replicating, thus killing them ......... For Wayne Green's
editorials - referring to Drs. Lyman and Kaali in 10/22/08 - among many
other interesting things CLICK HERE
http://www.waynegreen.com/wayne/news-archive_2008.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.hivwave.gr/pages/en/
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sie befinden sich hier: Seminare
und Vorträge /
Goodbye AIDS! Did it ever exist ?
Podiumsdiskussion zur Buchvorstellung
Athen, 7. April 2009, 12:30 Uhr
Thessaloniki, 8. April 2009, 19:30 Uhr
Teilnehmer sind Prof. Dr. Andrew Maniotis
(Medizinische Fakultät,
University of Illinois, Chicago), Janine Roberts
(Herausgeber der englischen Ausgabe), Lambros Papantoniou
(griechischer Pressekorrespondent in Washington), Juliane
Sacher (Fachärztin für Allgemeinmedizin, Frankfurt) und die Autorin
Maria Papagiannidou St-Pierre.
http://www.praxis-sacher.de/index.php?id=45&L=0
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.docgeorge.com/20080521174/Curing-Viruses-With-Electricity.html
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6,086,932.PN.&OS=PN/6,086,932&RS=PN/6,086,932
United States Patent 6,086,932
High electric pasteurization
Abstract Pasteurization and
sterilization of a flowable material such as food is performed by
means of pulsed electric field. The flowable material is passed
through a pair of closely spaced narrow electrodes at a high speed.
The electrodes are applied with a continuous high electric
potential. Because the material spends a very little time between
the electrodes, it experiences a short pulse of a high electric
field which electrocutes bacteria in the flowable material.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6,331,321.PN.&OS=PN/6,331,321&RS=PN/6,331,321
United States Patent
6,331,321 Robbins December 18,
2001
Process and apparatus
for reduction of microorganisms in a conductive medium using low
voltage pulsed electrical energy
Abstract
A process and apparatus are provided for reducing microorganisms in
a conductive medium using a low voltage pulsed electrical energy.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=6,787,105.PN.&OS=PN/6,787,105&RS=PN/6,787,105
United States Patent
6,787,105
Robbins September 7, 2004
Process and apparatus
for reduction of microorganisms in a conductive medium using low
voltage pulsed electrical energy
Abstract
A process and apparatus are provided for reducing microorganisms in
a conductive medium using a low voltage pulsed electrical energy.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=7,255,839.PN.&OS=PN/7,255,839&RS=PN/7,255,839
United States Patent
7,255,839 Chatroux ,
et al. August 14, 2007
Device and method for
treating a substance containing undesirable organisms using a pulsed
electrical field
Abstract
A device for treating a substance containing at least one
undesirable organism, using a pulsed electrical field. The device
includes at least one treatment zone of the substance located within
a passage zone associated with the substance. Each treatment zone is
only partially located within the associated passage zone. The
device also includes a mechanism to create movement for displacing
each treatment zone of the substance in the entire associated
passage zone.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=5,282,940.PN.&OS=PN/5,282,940&RS=PN/5,282,940
United States Patent 5,282,940
Griffis , et al. February 1, 1994
Method for reducing or eliminating
microorganisms in substances by electric stimulation
Abstract
A method for the reduction or elimination of microbes in liquid or
food products whereby the passage of a waveform, such as a DC
square-wave, of a specific amplitude, duty cycle and current through
the liquid or food product for a specific time period, allows for
the elimination of microbes such as Salmonella Typhimurium from a
variety of substances, including water, milk and solid food
products.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO1&Sect2=HITOFF&d=PALL&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsrchnum.htm&r=1&f=G&l=50&s1=5,514,391.PN.&OS=PN/5,514,391&RS=PN/5,514,391
United States Patent
5,514,391 Bushnell , et al. May 7, 1996
Process for reducing
levels of microorganisms in pumpable food products using a high
pulsed voltage system
Abstract
The present invention is directed to methods and apparatuses for
preserving fluid foodstuffs. More particularly, it is directed to
methods and apparatuses for extending the shelf life of perishable
fluid foodstuffs such as dairy products, fruit juices and liquid egg
products, which contain significant levels of microorganisms. The
improved methods and apparatuses incorporate a plurality of electric
field treatment zones with cooling units between each pair of
treatment zones in order to maintain the temperature of the pumpable
foodstuff at a level at which microorganisms are killed in
sufficient numbers and at which changes in the flavor, appearance,
odor, or functionality of the foodstuff remain within acceptable
ranges. For a comparable microorganism kill, foodstuffs prepared by
the present process have significantly higher quality than
foodstuffs prepared with standard thermal processes (e.g.,
ultra-high temperature pasteurization).
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CN 1623448
Prepolarized Pulse Electric Field Disinfectant Method and
its Equipment
Inventor: ZENG XINAN [CN] ; FU XIONG
Applicant: UNIV SOUTH CHINA TECH
2005-06-08
Inventor(s): ZENG XINAN [CN]; FU XIONG [CN]; YU SHUJUAN [CN]
Applicant(s): UNIV SOUTH CHINA TECH [CN]
Classification: - international: A23L3/00; A23L3/32; A23L3/00; A23L3/32;
(IPC1-7): A23L3/32; A23L3/00
Also published as: CN1285291 (C)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CN 1411871
Processor of Pulse Electric Field Sterilizing Equipment
Inventor: ZENG XIN AN [CN] ; LI GUOJI
Applicant: HUA NAN UNIV OF SCIENCE & ENGI
2003-04-23
Also published as: CN1194765 (C)
Abstract -- The present invention relates to a treatment device
of equipment for sterilizing liquid products in the fields of food,
biological, pharmaceutical and chemical industries by adopting
high-intensity pulse electric field. Said treatment device is formed from
material-treating cavity, two electrodes mounted in the material-treating
cavity, inlet and outlet, in which said material-treating cavity is vacuum
cavity, and can obtain good sterilizing effect.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CN1354018
High-voltage pulse electric field sterilization method and its equipment
Inventor: ZENG XIN AN [CN] ; FU XIONG
Applicant: HUA NAN UNIV OF SCIENCE & ENGI
2002-06-19
Also published as: CN1174691 (C)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"Engineering Aspects of Pulsed Electric Field
Pasteurization," Zhang, Qinghua, et al., Journal of Food Engineering,
25:261-281, 1994. .
"Inactivation of E. coli and S. cerevisiae by Pulsed
Electric Fields Under Controlled Temperature Conditions," Zhang, Q., et al.,
1994 American Society of Agricultural Engineers, vol. 37(2);581-587. .
"Inactivation of Microorganisms in a Semisolid Model Food
Using High Voltage Pulsed Electric Fields," Zhang, Qinghua, et al., Food
Science & Technology (lwt), 1994, 2(6):538..
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
US 5690978
HIGH VOLTAGE PULSED ELECTRIC FIELD TREATMENT CHAMBERS FOR THE
PRESERVATION OF LIQUID FOOD PRODUCTS
1998-04-09
Inventor(s): YIN YONGGUANG; ZHANG QINGHUA HOWARD; SASTRY SUDHIR KARTIKEYA
Applicant(s): OHIO STATE RES FOUND
Classification: - international: A23L3/00; A23L3/26; A23L3/32; A23L3/00;
A23L3/26; A23L3/32; (IPC1-7): A23L3/00; A23L3/26; A23L3/32 - European:
A23L3/00; A23L3/26; A23L3/32
Cited documents: US4723483 (A) US4838154 (A) US5235905 (A)
Abstract -- A pulsed electric field treatment device for the
sterilization and preservation of pumpable food products having at least two
electrodes (201, 203) and an insulator (202) and particularly suited for the
inactivation of vegetative and bacterial spore micro-organisms. Each
electrode includes an electrode flow chamber (207, 208) for making
electrical contact with the pumpable food product and for allowing the
pumpable food product to flow through the treatment devices. The insulator
(202) is situated between the electrodes (201, 203) and includes an
insulator flow chamber (206) positioned between the electrode flow chambers
(207, 208) and provides for the flow of pumpable food product from one
electrode flow chamber to the other. A high voltage pulse generator (107)
applies a high voltage signal of variable voltage, frequency and pulse
duration to the electrodes.; The electrode and insulator flow chambers may
employ a variety of sectional and cross-sectional geometries including
tubular, cylindrical, rectangular, elliptical and non-uniform design.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Biotechnol Bioeng. 1992 Dec
20;40(11):1412-20.
Kinetics of sterilization of Lactobacillus brevis cells by
the application of high voltage pulses.
Jayaram S, Castle GS, Margaritis A.
The technique of irreversible electroporation has been successfully applied
to cause a lethal effect on Lactobacillus
brevis cells suspended in phosphate buffer solution, Na(2)HPO(4)/NaH(2)PO(4)
. H(2)O (0.845/0.186 mM) between parallel plane
electrodes. Tests were carried out at different temperatures (24,45,60, and
80 degrees C) to determine if there was a
synergistic effect of temperature and electric pulse treatment on the
destruction of L. brevis. Experimental results indicate
that the viability (log N/N(0); where N(0) and N are the number of cells
survived per milliliter before and after pulse
voltage application, respectively) of L. brevis decreased with electric
field strength E and temperature T and treatment time
t(t). The relations between log(N/N(0)) and t(t) and log(N/N(0)) and E
indicate that higher field strengths are more
effective than higher treatment times in causing destruction of L. brevis
cells. It was also found that as the temperature of
the liquid medium containing L. brevis cells increased from 24 to 60 degrees
C, the death rate of L. brevis cells increased
with a decrease in the total treatment time t(t) (pulse width x number of
pulses applied). The application of an electric
field strength E = 25 kV/cm at 60 degrees C and treatment time t(t) = 10 ms
resulted in very high destruction levels of L.
brevis cells (N/N(0) = 10(-9)). In comparison with existing steam
sterilization technology, this new method of sterilization
using relatively low temperature and short treatment time could prove to be
an excellent method to minimize thermal
denaturation of important nutrient components in liquid media. (c) John
Wiley & Sons, Inc.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1996 Mar;45(1-2):148-57.
Killing of microorganisms by pulsed electric fields.
Grahl T, Märkl H.
Lethal effects of pulsed electric fields (PEF) on suspensions of various
bacteria, yeast, and spores in buffer solutions
and liquid foodstuffs were examined. Living-cell counts of vegetative cell
types were reduced by PEF treatment by up to more
than four orders of magnitude (> 99.99%). On the other hand, endo- and
ascospores were not inactivated or killed to any great
extent. The killing of vegetative cell types depends on the electrical field
strength of the pulses and on the treatment time
(the product of the pulse number and the decay time constant of the pulses).
For each cell type, a specific critical electric
field strength (Ec) and a specific critical treatment time (tc) were
determined. Above these critical values, the fractions
of surviving cells were reduced drastically. The "limits" Ec and tc depend
on the cell characteristics as well as on the type
of medium in which the cells are suspended. Especially in acid media living-cell
counts were sufficiently decreased at very
low energy inputs. In addition to the inactivation of microorganisms, the
effect of PEF on food components such as whey
proteins, enzymes and vitamins, and on the taste of foodstuffs was studied.
The degree of destruction of these food
components by PEF was very low or negligible. Moreover, no significant
deterioration of the taste of foodstuffs was detected
after PEF treatment. Disintegration of cells by PEF treatment in order to
harvest intracellular products was also studied.
Yeast cells, suspended in buffer solution, were not disintegrated by
electric pulses. Hence, PEF treatment is an excellent
process for inactivation of microorganisms in acid and in thermosensive
media, but not for complete disintegration of
microbial cells.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1996 Jul;36(6):603-27.
Nonthermal pasteurization of liquid foods using high-intensity
pulsed electric fields.
Qin BL, Pothakamury UR, Barbosa-Cánovas GV, Swanson BG.
Processing foods with high-intensity pulsed electric fields (PEF) is a new
technology to inactivate microorganisms and
enzymes with only a small increase in food temperature. The appearance and
quality of fresh foods are not altered by the
application of PEF, while microbial inactivation is caused by irreversible
pore formation and destruction of the
semipermeable barrier of the cell membrane. High-intensity PEF provides an
excellent alternative to conventional thermal
methods, where the inactivation of the microorganisms implies the loss of
valuable nutrients and sensory attributes. This
article presents recent advances in the PEF technology, including microbial
and enzyme inactivation, generation of pulsed
high voltage, processing chambers, and batch and continuous systems, as well
as the theory and its application to food
pasteurization. PEF technology has the potential to improve economical and
efficient use of energy, as well as provide
consumers with minimally processed, microbiologically safe, nutritious and
freshlike food products.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Food Prot. 1999 Sep;62(9):1088-96.
Pulsed electric field processing of foods: a review.
Jeyamkondan S, Jayas DS, Holley RA.
Use of pulsed electric fields (PEFs) for inactivation of microorganisms
is one of the more promising nonthermal
processing methods. Inactivation of microorganisms exposed to high-voltage
PEFs is related to the electromechanical
instability of the cell membrane. Electric field strength and treatment time
are the two most important factors involved in
PEF processing. Encouraging results are reported at the laboratory level,
but scaling up to the industrial level escalates
the cost of the command charging power supply and of the high-speed
electrical switch. In this paper, we critically review
the results of earlier experimental studies on PEFs and we suggest the
future work that is required in this field.
Inactivation tests in viscous foods and in liquid food containing
particulates must be conducted. A successful continuous PEF
processing system for industrial applications has yet to be designed. The
high initial cost of setting up the PEF processing
system is the major obstacle confronting those who would encourage the
system's industrial application. Innovative
developments in high-voltage pulse technology will reduce the cost of pulse
generation and will make PEF processing
competitive with thermal-processing methods.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int J Food Microbiol. 2000 Mar 10;54(1-2):91-8.
Pulsed electric fields inactivation of attached and free-living
Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua under several
conditions.
Dutreux N, Notermans S, Wijtzes T, Góngora-Nieto MM, Barbosa-Cánovas GV,
Swanson BG.
The use of pulsed electric fields (PEF) is considered as a mild process in
the inactivation of microorganisms present in
liquid food products. PEF treatments of Escherichia coli and Listeria
innocua suspended in milk and phosphate buffer, with
same pH and same conductivities, yielded to similar inactivation. Reduction
rates obtained in distilled water indicated that
conductivity of the food product is a main parameter in bacterial
inactivation. Bacteria attached to polystyrene beads were
inactivated by PEF at a greater (E. coli) or equal rate (L. innocua) than
free-living bacteria. Base on the use of selective
and non-selective enumeration media, no clear indications were obtained for
sublethal damage of microorganisms surviving the
PEF treatment. E. coli cells subjected to 60 pulses at 41 kV/cm were
examined by transmission and scanning electron
microscopy. Changes in the cytoplasm were observed and the cell surface
appeared rough. The cells outer membranes were
partially destroyed allowing leaking of cell cytoplasm.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Radiat Environ Biophys. 1981;20(1):53-65.
Killing of bacteria with electric pulses of high field strength.
Hülsheger H, Potel J, Niemann EG.
Bacteria of the type E. coli K12 have been treated in experiments using high-voltage
pulses of short time (microseconds)
as a killing agent. The role of different experimental parameters has been
studied: kind of electrolyte, concentration,
length of pulses, field strength, pH and temperature. Electrolytes with
bivalent cations were found to reduce the lethal
action. the relative rate of killed bacteria was shown to be mainly governed
by the field strength and the treatment time,
which is defined by the product of pulse number and decay time constant.
From the obtained results a function has been
developed which enables the precalculation of the killing rate for E. coli,
provided that certain limits of experimental
conditions are considered. No correlation between the applied electric
energy and the lethal effect could be found.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Radiat Environ Biophys. 1980;18(4):281-8.
Lethal effects of high-voltage pulses on E. coli K12.
Hülsheger H, Niemann EG.
The lethal effects of high-voltage capacitor-discharges in suspensions of E.
coli K12 with varying electrolytes have been examined. A reduction of more
than 99.9% of living cells, dependent on the applied voltage could be proved.
The bactericidal action is assumed to be due to direct effects of high
electric fields. Electrolytically produced chlorine was shown to act as an
additional toxic agent, when chloride is present in the treated medium. The
relative survival rate of bacteria has been found to depend also on the
concentration of cells during pulse treatment.
-------------------------------------------------------
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1996 Mar;45(1-2):148-57.
Killing of microorganisms by pulsed electric fields.
Grahl T, Märkl H.
Technische Universität Hamburg-Harburg, Germany.
Lethal effects of pulsed electric fields (PEF) on suspensions of various
bacteria, yeast, and spores in buffer solutions and liquid foodstuffs were
examined. Living-cell counts of vegetative cell types were reduced by PEF
treatment by up to more than four orders of magnitude (> 99.99%). On the
other hand, endo- and ascospores were not inactivated or killed to any great
extent. The killing of vegetative cell types depends on the electrical field
strength of the pulses and on the treatment time (the product of the pulse
number and the decay time constant of the pulses). For each cell type, a
specific critical electric field strength (Ec) and a specific critical
treatment time (tc) were determined. Above these critical values, the
fractions of surviving cells were reduced drastically. The "limits" Ec and
tc depend on the cell characteristics as well as on the type of medium in
which the cells are suspended. Especially in acid media living-cell counts
were sufficiently decreased at very low energy inputs. In addition to the
inactivation of microorganisms, the effect of PEF on food components such as
whey proteins, enzymes and vitamins, and on the taste of foodstuffs was
studied. The degree of destruction of these food components by PEF was very
low or negligible. Moreover, no significant deterioration of the taste of
foodstuffs was detected after PEF treatment. Disintegration of cells by PEF
treatment in order to harvest intracellular products was also studied. Yeast
cells, suspended in buffer solution, were not disintegrated by electric
pulses. Hence, PEF treatment is an excellent process for inactivation of
microorganisms in acid and in thermosensive media, but not for complete
disintegration of microbial cells.
---------------------------------------------------
J Appl Microbiol. 2003;94(4):571-9.
Modelling and optimization of inactivation of Lactobacillus plantarum by
pulsed electric field treatment.
Abram F, Smelt JP, Bos R, Wouters PC.
Food Processing Group, Unilever Research & Development Vlaardingen, The
Netherlands.
AIMS: The effect of critical pulsed electric field (PEF) process parameters,
such as electric field strength, pulse length and number of pulses, on
inactivation of Lactobacillus plantarum was investigated. METHODS AND
RESULTS: Experiments were performed in a pH 4.5 sodium phosphate buffer
having a conductivity of 0.1 S m-1, using a laboratory-scale continuous PEF
apparatus with a co-linear treatment chamber. An inactivation model was
developed as a function of field strength, pulse length and number of
pulses. Based on this inactivation model, the conditions for a PEF treatment
were optimized with respect to the minimum energy required to obtain a
certain level of inactivation. It was shown that the least efficient process
parameter in the range investigated was the number of pulses. The most
efficient way to optimize inactivation of Lact. plantarum was to increase
the field strength up to 25.7 kV cm-1, at the shortest pulse length
investigated, 0.85 micros, and using a minimum number of pulses. The highest
inactivation of Lact. plantarum at the lowest energy costs is obtained by
using the equation: E=26.7tau0.23, in which E is the field strength and tau
the pulse length. An optimum is reached by substituting tau with 5.1.
CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrates that the correct choice of parameters,
as predicted by the model described here, can considerably improve the PEF
process. SIGNIFICANCE AND IMPACT OF THE STUDY: The knowledge gained in this
study improves the understanding of the limitations and opportunities of the
PEF process. Consequently, the advantage of the PEF process as a new option
for non-thermal decontamination can be better utilized.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
J Food Prot. 2001 Jul;64(7):964-9.
Reduction in levels of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in apple cider by pulsed
electric fields.
Iu J, Mittal GS, Griffiths MW.
Department of Food Science, University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada.
Many studies have demonstrated that high voltage pulsed electric field (PEF)
treatment has lethal effects on microorganisms including Escherichia coli
O157:H7; however, the survival of this pathogen through the PEF treatment is
not fully understood. Fresh apple cider samples inoculated with E. coli
O157:H7 strain EC920026 were treated with 10, 20, and 30 instant charge
reversal pulses at electric field strengths of 60, 70, and 80 kV/cm, at 20,
30, and 42 degrees C. To accurately evaluate the lethality of apple cider
processing steps, counts were determined on tryptic soy agar (TSA) and
sorbitol MacConkey agar (SMA) to estimate the number of injured and
uninjured E. coli O157:H7 cells after PEF treatment. Cell death increased
significantly with increased temperatures and electric field strengths. A
maximum of 5.35-log10 CFU/ml (P < 0.05) reduction in cell population was
achieved in samples treated with 30 pulses and 80 kV/cm at 42 degrees C.
Cell injury measured by the difference between TSA and SMA counts was found
to be insignificant (P > 0.05). Under extreme conditions, a 5.91-log10 CFU/ml
reduction in cell population was accomplished when treating samples with 10
pulses and 90 kV/cm at 42 degrees C. PEF treatment, when combined with the
addition of cinnamon or nisin, triggered cell death, resulting in a
reduction in E. coli O157:H7 count of 6 to 8 log10 CFU/ml. Overall, the
combination of PEF and heat treatment was demonstrated to be an effective
pasteurization technique by sufficiently reducing the number of viable E.
coli O157:H7 cells in fresh apple cider to meet U.S. Federal Drug
Administration recommendations.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Food Prot. 1999 Jul;62(7):793-6.
Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Escherichia coli 8739 in apple
juice by pulsed electric fields.
Evrendilek GA, Zhang QH, Richter ER.
Department of Food Science and Technology, The Ohio State University,
Columbus 43210, USA.
The effect of high voltage pulsed electric field (PEF) treatment on
Escherichia coli O157:H7 and generic E. coli 8739 in apple juice was
investigated. Fresh apple juice samples inoculated with E. coli O157:H7 and
E. coli 8739 were treated by PEF with selected parameters including electric
field strength, treatment time, and treatment temperature. Samples were
exposed to bipolar pulses with electric field strengths of 30, 26, 22, and
18 kV/cm and total treatment times of 172, 144, 115, and 86 micros. A 5-log
reduction in both cultures was determined by a standard nonselective medium
spread plate laboratory procedure. Treatment temperature was kept below 35
degrees C. Results showed no difference in the sensitivities of E. coli
O157:H7 and E. coli 8739 against PEF treatment. PEF is a promising
technology for the inactivation of E. coli O157:H7 and E. coli 8739 in apple
juice.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int J Food Microbiol. 2000 Apr 10;55(1-3):143-6.
Influence of different factors on the inactivation of Salmonella senftenberg
by pulsed electric fields.
Alvarez I, Raso J, Palop A, Sala FJ.
Tecnología de los Alimentos, Dpto. PACA, Facultad de Veterinaria,
Universidad de Zaragoza, Spain.
The influence of growth phase, cell concentration, pH and conductivity of
treatment medium on the inactivation of Salmonella senftenberg by high
electric field pulses (HELP) was studied. Cells were more resistant to HELP
treatments at the beginning of the logarithmic phase and at the stationary
phase. Microbial inactivation was not a function of the initial cell
concentration. At constant input voltage, electric field strength obtained
in the treatment chamber depended on medium conductivity. At the same
electric field strength, conductivity did not influence S. senftenberg
inactivation. At the same conductivity, inactivation of S. senftenberg was
bigger at neutral than acidic pH.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Food Prot. 2003 Jun;66(6):1007-12.
Weibull distribution function based on an empirical mathematical model for
inactivation of Escherichia coli by pulsed electric fields.
Rodrigo D, Barbosa-Cánovas GV, Martínez A, Rodrigo M.
Instituto de Agroquímica y Tecnología de Alimentos, Consejo Superior de
Investigaciones Científicas, Apartado de Correos 73, 46100 Burjassot,
Valencia, Spain.
The pulsed electric field inactivation kinetics of Escherichia coli
suspended in orange juices with three different concentrations of carrot
juice (0, 20, and 60%) was studied. Electric field strengths ranged from 25
to 40 kV/cm, and treatment times ranged from 40 to 340 micros. Experimental
data were fitted to Bigelow, Hülsheger, and Weibull distribution functions,
and the Weibull function provided the best fit (with the lowest mean square
error). The dependency of each model's kinetic constant on electric field
strength and carrot juice concentration was studied. A secondary model was
developed to describe the relationship of Weibull parameters a and n to
electric field strength and carrot juice concentration. An empirical
mathematical model based on the Weibull distribution function, relating the
natural logarithm of the survival fraction to treatment time, electric field
strength, and carrot juice concentration, was developed. Parameters were
estimated by a nonlinear regression. The results of this study indicate that
the error rate for the model's predictions was 6.5% and that the model was
suitable for describing E. coli inactivation.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Dec;65(12):5364-71.
Effects of pulsed electric fields on inactivation kinetics of Listeria
innocua.
Wouters PC, Dutreux N, Smelt JP, Lelieveld HL.
Microbiology & Preservation, Unilever Research Vlaardingen, 3133 AT
Vlaardingen, The Netherlands. Patrick.Wouters@Unilever.com
The effects of pulsed electric field (PEF) treatment and processing factors
on the inactivation kinetics of Listeria innocua NCTC 11289 were
investigated by using a pilot plant PEF unit with a flow rate of 200
liters/h. The electric field strength, pulse length, number of pulses, and
inlet temperature were the most significant process factors influencing the
inactivation kinetics. Product factors (pH and conductivity) also influenced
the inactivation kinetics. In phosphate buffer at pH 4.0 and 0.5 S/m at 40
degrees C, a 3. 0-V/microm PEF treatment at an inlet temperature of 40
degrees C resulted in > or = 6.3 log inactivation of strain NCTC 11289 at
49.5 degrees C. A synergistic effect between temperature and PEF
inactivation was also observed. The inactivation obtained with PEF was
compared to the inactivation obtained with heat. We found that heat
inactivation was less effective than PEF inactivation under similar time and
temperature conditions. L. innocua cells which were incubated for a
prolonged time in the stationary phase were more resistant to the PEF
treatment, indicating that the physiological state of the microorganism
plays a role in inactivation by PEF. Sublethal injury of cells was observed
after PEF treatment, and the injury was more severe when the level of
treatment was increased. Overall, our results indicate that it may be
possible to use PEF in future applications in order to produce safe
products.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Food Prot. 1998 Sep;61(9):1203-6.
Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in milk by pulsed electric field.
Reina LD, Jin ZT, Zhang QH, Yousef AE.
Department of Food Science and Technology, Ohio State University, Columbus
43210, USA.
Pasteurized whole, 2%, and skim milk were inoculated with Listeria
monocytogenes Scott A and treated with high-voltage pulsed electric field (PEF).
The effects of milk composition (fat content) and PEF parameters (electric
field strength, treatment time, and treatment temperature) on the
inactivation of the bacterium were studied. No significant differences were
observed in the inactivation of L. monocytogenes Scott A in three types of
milk by PEF treatment. With treatment at 25 degrees C, 1- to 3-log
reductions of L. monocytogenes were observed. PEF lethal effect was a
function of field strength and treatment time. Higher field strength or
longer treatment time resulted in a greater reduction of viable cells. A
4-log reduction of the bacterium was obtained by increasing the treatment
temperature to 50 degrees C. Results indicate that the use of a high-voltage
PEF is a promising technology for inactivation of foodborne pathogens.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Biotechnol Bioeng. 1992 Dec 20;40(11):1412-20.
Kinetics of sterilization of Lactobacillus brevis cells by the application
of high voltage pulses.
Jayaram S, Castle GS, Margaritis A.
Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Western Ontario, London,
Ontario, Canada N6A 5B9.
The technique of irreversible electroporation has been successfully applied
to cause a lethal effect on Lactobacillus brevis cells suspended in
phosphate buffer solution, Na(2)HPO(4)/NaH(2)PO(4) . H(2)O (0.845/0.186 mM)
between parallel plane electrodes. Tests were carried out at different
temperatures (24,45,60, and 80 degrees C) to determine if there was a
synergistic effect of temperature and electric pulse treatment on the
destruction of L. brevis. Experimental results indicate that the viability (log
N/N(0); where N(0) and N are the number of cells survived per milliliter
before and after pulse voltage application, respectively) of L. brevis
decreased with electric field strength E and temperature T and treatment
time t(t). The relations between log(N/N(0)) and t(t) and log(N/N(0)) and E
indicate that higher field strengths are more effective than higher
treatment times in causing destruction of L. brevis cells. It was also found
that as the temperature of the liquid medium containing L. brevis cells
increased from 24 to 60 degrees C, the death rate of L. brevis cells
increased with a decrease in the total treatment time t(t) (pulse width x
number of pulses applied). The application of an electric field strength E =
25 kV/cm at 60 degrees C and treatment time t(t) = 10 ms resulted in very
high destruction levels of L. brevis cells (N/N(0) = 10(-9)). In comparison
with existing steam sterilization technology, this new method of
sterilization using relatively low temperature and short treatment time
could prove to be an excellent method to minimize thermal denaturation of
important nutrient components in liquid media. (c) John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int J Food Microbiol. 2004 May 15;93(1):1-10.
Growth of pulsed electric field exposed Escherichia coli in relation to
inactivation and environmental factors.
Aronsson K, Borch E, Stenlöf B, Rönner U.
SIK, The Swedish Institute for Food and Biotechnology, Box 5401, 402 29
Göteborg, Sweden.
Pulsed electric fields (PEF) have been proven to inactivate
microorganisms during nonthermal conditions and have the potential to
replace thermal processing as a method for food preservation. However, there
is a need to understand the recovery and growth of survivors and potentially
injured microorganisms following PEF processing. The purpose of this
investigation was to study the growth of Escherichia coli at 10 degrees C
following exposure to electrical field strengths (15, 22.5 and 30 kV/cm) in
relation to inactivation and the amount of potentially sublethally injured
cells. One medium was used as both a treatment medium and an incubation
medium, to study the influence of environmental factors on the inactivation
and the growth of the surviving population. The pH (5.0, 6.0 and 7.0) and
water activity (1.00, 0.985 and 0.97) of the medium was varied by adding HCl
and glycerol, respectively. Growth was followed continuously by measuring
the optical density. The time-to-detection (td) and the maximum specific
growth rate (micromax) were calculated from these data. Results showed that
the PEF process did not cause any obvious sublethal injury to the E. coli
cells. The number of survivors was a consequence of the combination of
electrical field strength and environmental factors, with pH being the most
prominent. Interestingly, the micromax of subsequent growth was influenced
by the applied electrical field strength during the process, with an
increased micromax at more intense electrical field strengths. In addition,
the micromax was also influenced by the pH and water activity. The td, which
could theoretically be considered as an increase in shelf life, was found to
depend on a complex correlation between electrical field strength, pH and
water activity. That could be explained by the fact that the td is a
combination of the number of survivors, the recovery of sublethal injured
cells and the growth rate of the survivors. Copyright 2003 Elsevier B.V.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Appl Microbiol. 2005;99(1):94-104.
Occurrence of sublethal injury after pulsed electric fields depending on
the micro-organism, the treatment medium ph and the intensity of the
treatment investigated.
García D, Gómez N, Mañas P, Condón S, Raso J, Pagán R.
Departamento de Producción Animal y Ciencia de los Alimentos, Facultad de
Veterinaria, Universidad de Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain.
AIMS: The objective was to investigate the occurrence of sublethal injury
after pulsed electric field (PEF) depending on the treatment time, the
electric field strength and the pH of the treatment media in two
Gram-positive (Bacillus subtilis ssp. niger, Listeria monocytogenes) and six
Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Escherichia coli O157:H7, Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, Salmonella serotype Senftenberg 775W, Salmonella serotype
Typhimurium, Yersinia enterocolitica) bacterial strains. METHODS AND
RESULTS: A characteristic behaviour was observed for the Gram-positive and
Gram-negative bacteria studied. Whereas Gram-positive bacteria showed a
higher PEF resistance at pH 7.0, the Gram-negative were more resistant at pH
4.0. In these conditions, in which bacteria showed their maximum resistance,
a large proportion of sublethally injured cells were detected. In most
cases, the longer the treatment time and the higher the electric field
applied, the greater the proportion of sublethally injured cells that were
detected. No sublethal injury was detected when Gram-positive bacteria were
treated at pH 4.0 and Gram-negative at pH 7.0. CONCLUSIONS: Sublethal injury
was detected after PEF so, bacterial inactivation by PEF is not an 'all or
nothing' event. SIGNIFICANCE AND IMPACT OF THE STUDY: This work could be
useful for improving food preservation by PEF.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Jan 12;1278(1):79-88.
Contribution to the biophysics of the lethal effects of electric field on
microorganisms.
Kekez MM, Savic P, Johnson BF.
National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, Canada.
The proposed model assumes that the criteria leading to the lethal breakdown
of microorganisms suspended in a continuous medium depend on two parameters:
(a) the applied electric field must exceed the critical field of membrane to
create holes and (b) the Joule energy (deposited in the membrane) must
exceed the minimum value beyond which the cell can not recover. The first
parameter initiates (reversible) breakdown and the second one, the
completion of the (irreversible) electrical breakdown leading to death of
the cell. The number of cells surviving the electric field treatment is
related to statistical distribution of cell size. Comparison between theory
and the experimental results of Kinosita and Tsong (1977); Hülsheger et al.
(1980, 1981, 1983); Rosemberg and Korenstein (1990) and others is given.
PMID: 8611611 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Water Health. 2004 Dec;2(4):267-77.
The effectiveness of a multi-spark electric discharge system in the
destruction of microorganisms in domestic and industrial wastewaters.
Anpilov AM, Barkhudarov EM, Christofi N, Kop'ev VA, Kossyi IA, Taktakishvili
MI, Zadiraka YV.
General Physics Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 38 Vavilov
Street, Moscow, Russia.
The aim of this work was to investigate the effectiveness of a high voltage
multi-spark electric discharge, with pulse energy of 1 Joule, in killing
microorganisms in wastewater. Wastewater from primary treated effluent
arising from domestic and industrial sources was abstracted for continuous
pulsed discharge disinfection. The wastewater contained a large mixed
population of microorganisms (approximately 10(7) CFU ml(-1) [10(9) CFU 100
ml(-1)] total aerobic heterotrophic bacteria) including vegetative cells and
spores. The electrical conductivity of the wastewater ranged from 900-1400
microS cm(-1) and it was shown that a specific energy of 1.25-1.5 J cm(-3)
was required to achieve 1 log reduction in bacterial (faecal coliforms/total
aerobic heterotrophs) content. This is higher than that previously shown to
reduce the population of E. coli in tap water of low conductivity,
demonstrating the role of total wastewater constituents, including dissolved
and particulate substances, water colour and the presence of microbial
spores, in effective disinfection. The system can be engineered to eradicate
microbial populations to levels governed by legislation by increasing
treatment time or energy input.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Food Prot. 1999 Dec;62(12):1381-6.
High intensity pulsed electric fields applied to egg white: effect on
Salmonella Enteritidis inactivation and protein denaturation.
Jeantet R, Baron F, Nau F, Roignant M, Brulé G.
Laboratoire de Technologie Alimentaire, Ecole Nationale Supérieure
Agronomique, Rennes, France. jeantet@agrorennes.educagri.fr
High-intensity electric fields have been successfully applied to the
destruction of Salmonella Enteritidis in diaultrafiltered egg white. The
effects of electric field strength (from 20 to 35 kV x cm(-1)), pulse
frequency (from 100 to 900 Hz), pulse number (from 2 to 8), temperature
(from 4 to 30 degrees C), pH (from 7 to 9), and inoculum size (from 10(3) to
10(7) CFU x ml(-1)) were tested through a multifactorial experimental
design. Experimental results indicate that, for Salmonella inactivation, the
electric field intensity is the dominant factor with a strongly positive
effect, strengthened by its positive interaction with pulse number. Pulse
number, temperature, and pH have also significant positive effects but to a
lesser extent. In the most efficient conditions, the pulsed electric field (PEF)
treatment is capable of 3.5 log10 reduction in viable salmonellae.
Simultaneously, the measure of surface hydrophobicity does not indicate any
increase after PEF treatment. These results suggest that no protein
denaturation occurs, unlike what is observed after comparable heat treatment
in terms of Salmonella inactivation (55 degrees C for 15 min).
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Dec;38(12):2803-9.
Mechanism of electrical enhancement of efficacy of antibiotics in killing
biofilm bacteria.
Costerton JW, Ellis B, Lam K, Johnson F, Khoury AE.
Center for Biofilm Engineering Montana State University, Bozeman.
59717-0398.
The bioelectric effect, in which electric fields are used to enhance the
efficacy of biocides and antibiotics in killing biofilm bacteria, has been
shown to reduce the very high concentrations of these antibacterial agents
needed to kill biofilm bacteria to levels very close to those needed to kill
planktonic (floating) bacteria of the same species. In this report, we show
that biofilm bacteria are readily killed by an antibiotic on all areas of
the active electrodes and on the surfaces of conductive elements that lie
within the electric field but do not themselves function as electrodes.
Considerations of electrode geometry indicate that very low (< 100 microA/cm2)
current densities may be effective in this electrical enhancement of
antibiotic efficacy against biofilm bacteria, and flow experiments indicate
that this bioelectric effect does not appear to depend entirely on the
possible local electrochemical generation of antibacterial molecules or
ions. These data are expected to facilitate the use of the bioelectric
effect in the prevention and treatment of device-related bacterial
infections that are caused by bacteria that grow in biofilms and thereby
frustrate antibiotic chemotherapy.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Dec;48(12):4662-4.
A radio frequency electric current enhances antibiotic efficacy against
bacterial biofilms.
Caubet R, Pedarros-Caubet F, Chu M, Freye E, de Belém Rodrigues M, Moreau JM,
Ellison WJ.
Unité Sécurité Microbiologique des Aliments, Institut des Sciences et
Techniques des Aliments de Bordeaux, Université de Bordeaux 1, Talence,
France. r.caubet@istab.u-bordeaux1.fr
Bacterial biofilms are notably resistant to antibiotic prophylaxis. The
concentration of antibiotic necessary to significantly reduce the number of
bacteria in the biofilm matrix can be several hundred times the MIC for the
same bacteria in a planktonic phase. It has been observed that the addition
of a weak continuous direct electric current to the liquid surrounding the
biofilm can dramatically increase the efficacy of the antibiotic. This
phenomenon, known as the bioelectric effect, has only been partially
elucidated, and it is not certain that the electrical parameters are
optimal. We confirm here the bioelectric effect for Escherichia coli
biofilms treated with gentamicin and with oxytetracycline, and we report a
new bioelectric effect with a radio frequency alternating electric current
(10 MHz) instead of the usual direct current. None of the proposed
explanations (transport of ions within the biofilm, production of additional
biocides by electrolysis, etc.) of the direct current bioelectric effect are
applicable to the radio frequency bioelectric effect. We suggest that this
new phenomenon may be due to a specific action of the radio frequency
electromagnetic field upon the polar parts of the molecules forming the
biofilm matrix.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lab Chip. 2005 Sep;5(9):943-8. Epub 2005 Jul 26.
A new pulsed electric field microreactor: comparison between the laboratory
and microtechnology scale.
Fox M, Esveld E, Luttge R, Boom R.
Food and Bioprocess Engineering Group, Wageningen University, P.O. Box 8129,
6700 EV, Wageningen, The Netherlands. Martijn.Fox@wur.nl
This paper presents a new microreactor dedicated for pulsed electric field
treatment (PEF), which is a pasteurization method that inactivates
microorganisms with short electric pulses. The PEF microreactor consists of
a flow-through channel with a constriction where the electric field is
focussed. Compared to a laboratory-scale setup 25 times lower voltages were
needed to obtain the same electric field strength due to the close electrode
spacing. A finite element model showed that the electric field intensity is
very homogeneous throughout the channel, which is crucial for the
pasteurization processes. Experiments where artificial vesicles, loaded with
carboxyfluorescein, were electroporated showed that the maximum
transmembrane potential adequately described the processes both in the
microreactor and the laboratory-scale setup, although the length scales are
different. Electroporation started at a transmembrane potential of 0.5 V,
reaching a maximum fraction of electroporated vesicles of 51% at a
transmembrane potential of 1.5 V. The partial electroporation is not a
result of the heterogenity of the vesicles or the electric field. With this
new PEF microreactor it is possible to study the PEF process in more detail.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Anticancer Res. 2001 May-Jun;21(3B):1809-15.
A new antitumour treatment combining radiation and electric pulses.
Engström PE, Persson BR, Brun A, Salford LG.
Department of Radiation Physics, Lund University Hospital, Sweden.
AIM: To investigate the antitumour effect of radiation in combination with
electropermeabilization on subcutaneous rat glioma tumours. MATERIALS AND
METHODS: Sub-optimal radiation treatment was administered separately or in
combination with electric pulses of high voltage to subcutaneous rat brain
tumours. The treatment was repeated on four consecutive days and evaluated
by TGD and microscopical examination. The tumours were stained for Factor
VlII/von Willebrand Factor to investigate the effects on the tumour
vasculature. RESULTS: Radiation and electric pulses applied concomitantly
resulted in a cure rate of 67% (tumour free >80 days after treatment).
Radiation-treated animals showed progressive disease. Histological and
immunohistochemical examination of electric impulse-treated tumours showed
instant and severe deteriorating effects on tumour vasculature. CONCLUSION:
A distinct antitumour effect of the combined treatment of electric pulses
and radiation treatment was observed. We believe that the tumouricidal
effect arises from destruction of the tumour vasculature but also from DNA
related damage from reactive oxygen formed by the electric pulses and the
radiation treatment.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int J Food Microbiol. 2003 Oct 15;87(1-2):87-95.
The influence of process parameters for the inactivation of Listeria
monocytogenes by pulsed electric fields.
Alvarez I, Pagán R, Condón S, Raso J.
Tecnología de los Alimentos, Facultad de Veterinaria, Universidad de
Zaragoza, 50.013 Saragossa, Spain.
The influence of the electric field strength, the treatment time, the total
specific energy and the conductivity of the treatment medium on the Listeria
monocytogenes inactivation by pulsed electric fields (PEF) has been
investigated. L. monocytogenes inactivation increased with the field
strength, treatment time and specific energy. A maximum inactivation of 4.77
log(10) cycles was observed after a treatment of 28 kV/cm, 2000 micros and
3490 kJ/kg. The lethal effect of PEF treatments on L. monocytogenes was not
influenced by the conductivity of the treatment medium in a range of 2, 3
and 4 mS/cm when the total specific energy was used as a PEF control
parameter. A mathematical model based on the Weibull distribution was fitted
to the experimental data when the field strength (15-28 kV/cm), treatment
time (0-2000 micros) and specific energy (0-3490 kJ/kg) were used as PEF
control parameters. A linear relationship was obtained between the log(10)
of the scale factor (b) and the electric field strength when the treatment
time and the total specific energy were used to control the process. The
total specific energy, in addition to the electric field strength and the
treatment time, should be reported in order to evaluate the microbial
inactivation by PEF.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Water Res. 2002 Aug;36(14):3429-38.
Elimination of free-living amoebae in fresh water with pulsed electric
fields.
Vernhes MC, Benichou A, Pernin P, Cabanes PA, Teissié J.
Institut de Pharmacologic et de Biologie Structurale, CNRS UMR 5089,
Toulouse, France.
This study investigates the effects of pulsed electric fields on the
inactivation of trophozoite form of Naegleria lovaniensis Ar9M-1 in batch
and flow processes, systematically examining the lethal effect of field
strength, pulse duration, number of pulses, and pulse frequency. Our results
show that amoebae eradication is modulated by pulse parameters, composition
of the pulsing medium, and physiological state of the cells. Cell survival
is not related to the energy delivered to the cell suspension during the
electrical treatment. For a given energy a strong field applied for a short
cumulative pulse duration affects viability more than a weak field with a
long cumulative pulsation. We also determine the optimal electrical
conditions to obtain an inactivation rate higher than 95% while using the
least energy. Flow processes allow to treat large-scale volumes. Our results
show that the most efficient flow process for amoeba eradication requires a
field parallel to the flow. Pulsed electric fields are a new and attractive
method for inactivating amoebae in large volumes of fresh water.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
J Dairy Sci. 2006 Mar;89(3):905-11.
Comparative study on shelf life of whole milk processed by high-intensity
pulsed electric field or heat treatment.
Odriozola-Serrano I, Bendicho-Porta S, Martín-Belloso O.
Department of Food Technology UTPV-CeRTA, University of Lleida Rovira Roure
191, 25198 Lleida, Spain.
The effect of high-intensity pulsed electric fields (HI-PEF) processing
(35.5 kV/cm for 1,000 or 300 micros with bipolar 7-micros pulses at 111 Hz;
the temperature outside the chamber was always < 40 degrees C) on microbial
shelf life and quality-related parameters of whole milk were investigated
and compared with traditional heat pasteurization (75 degrees C for 15 s),
and to raw milk during storage at 4 degrees C. A HIPEF treatment of 1,000
micros ensured the microbiological stability of whole milk stored for 5 d
under refrigeration. Initial acidity values, pH, and free fatty acid content
were not affected by the treatments; and no proteolysis and lipolysis were
observed during 1 wk of storage in milk treated by HIPEF for 1,000 micros.
The whey proteins (serum albumin, beta-lactoglobulin, and alpha-lactalbumin)
in HIPEF-treated milk were retained at 75.5, 79.9, and 60%, respectively,
similar to values for milk treated by traditional heat pasteurization.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lett Appl Microbiol. 2002;35(1):90-4.
Pulsed high voltage electric discharge disinfection of microbially
contaminated liquids.
Anpilov AM, Barkhudarov EM, Christofi N, Kop'ev VA, Kossyi IA, Taktakishvili
MI, Zadiraka Y.
General Physics Institute, Moscow, Russia.
AIMS: To examine the use of a novel multielectrode slipping surface
discharge (SSD) treatment system, capable of pulsed plasma discharge
directly in water, in killing micro-organisms. METHODS AND RESULTS: Potable
water containing Escherichia coli and somatic coliphages was treated with
pulsed electric discharges generated by the SSD. The SSD system was highly
efficient in the microbial disinfection of water with a low energy
utilization (eta approximately 10-4 kW h l-1). CONCLUSIONS: The SSD
treatment was effective in the destruction of E. coli and its coliphages
through the generation of u.v. radiation, ozone and free radicals.
SIGNIFICANCE AND IMPACT OF THE STUDY: The non-thermal treatment method can
be used for the eradication of micro-organisms in a range of contaminated
liquids, including milk, negating the use of pasteurization. The method
utilizes multipoint electric discharges capable of treating large volumes of
liquid under static and flowing regimes.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2004 Nov;380(5-6):831-7.
Simultaneous determination of multiple constituents in real beer samples of
different origins by capillary zone electrophoresis.
Cortacero-Ramírez S, Segura-Carretero A, Cruces-Blanco C, Romero-Romero ML,
Fernández-Gutiérrez A.
Research Laboratories of Grupo Cervezas Alhambra, S.L. Avda. Murcia 1, 18010
Granada, Spain.
Simultaneous determination of alcohols, amines, amino acids, flavonoids, and
purine and pyrimidine bases in bottled beer samples directly without any
pre-treatment was carried out by capillary zone electrophoresis with
diode-array detection. Electrolyte conditions such as pH, composition and
concentration of the buffer, working voltage and type and time of injection
were checked. The best separation of the cited analytes was achieved in 70
mM sodium borate solution and pH 10.25. The detection limits were from 2.1
to 5.6 mg L(-1) for the 18 compounds studied. The developed method is rapid,
sensitive and quantitative and has been applied to seven types of
international bottled beers of different origins bought locally.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Endod Dent Traumatol. 1985 Jun;1(3):112-5.
Effect of electric current and silver electrodes on oral bacteria.
Tronstad L, Trope M, Hammond BF.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 1992 Oct;17(10):604-6, 639.
Research on sterilization of pathogens by high electrostatic voltage method
Wang X, Wu Y, Ni X, Xia B, Xu J, Du Q.
Institute of Electrostatics, Northeast Normal University, Changchun.
An experimental research has been carried out on the sterilization of four
kinds of pathogens by high electrostatic method along with an inquiry into
the influence of voltage waveform and the treated time on sterilization. It
is concluded that pathogens can be killed efficiently by corona discharge
field.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9151574
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11588820?dopt=Abstract
:
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll.
2001 May;42(2):97-100.
Effect of weak electric current on reducing oral bacteria
in vitro.
Ichimura K,
Harazaki M,
Yanagi K,
Isshiki Y.
Department of Orthodontics, Tokyo Dental College, 1-2-2 Masago, Mihama-ku,
Chiba 261-8502, Japan.
The ions generated by weak electric current may be used for removal of
dental plaque. Also, it has been judged from changes in the viable bacterial
cell count and the amount of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the saliva that
the passage of such a current also has a bactericidal effect on the oral
microflora. We confirmed in vitro that 0.5 and 1.0 mA currents that passed
for 10 min through phosphate buffered saline containing salivary bacteria
were effective in killing the bacteria.
PMID: 11588820 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Appl Environ
Microbiol.
2004 June;
70(6):
3781–3784.
doi:
10.1128/AEM.70.6.3781-3784.2004.
|
PMCID: PMC427729
|
Copyright © 2004, American Society for Microbiology
Received August 22, 2003; Accepted March 8, 2004.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Biocompatible electric current attenuates HIV
infectivity http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15858720?dopt=Abstract
click
here
or here, for the saved page
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BIOCOMPATIBLE ELECTRIC CURRENT
ATTENUATES HIV-I INFECTIVITY
William D. Lyman, Irwin R.Merkatz
William C. Hatch and Steven C. Kaali
Departments of Pathology,
and Obstetrics & Gynecology
Albert Einstein. College of Medicine,
1300 Morris Park Ave., Bronx, N.Y.10461
Running title: Electricity reduces HIV-1 infectivity
Correspondence: Dr, Wm.. D. Lyman
Department of Pathology
Albert Einstein College of Medicine
1300 Morris Park Avenue
The Bronx, NY 10461
(212) 430-2171
SUMMARY
In this report, we present the results of double-blinded studies
on the use of direct electric current to alter the infectivity o£ HIV-1 for susceptible
cells in vitro. Two lymphoblastoid cell lines (H9 and CEM-SS) were exposed
to aliquots of the RT strain of HIV-1 treated with direct current. Results of these
studies show that virus treated with currents from 50 to 100 microamperes (μA) has a
significantly reduced infectivity for susceptible cells.
These experimental currents were equal to 3.85 and 7.7.μΑ/mm2
current densities respectively. The reduction of infectivity was dependent upon, the total
electric charge (μA x min) passing through the chamber to which the virus was exposed.
Viral infectivity was determined by two independent measures: a syncytium-formation assay
which can be used to quantify the production of infectious particles; and. a reverse
transcriptase assay which is an index of viral protein production. Additional experiments
demonstrated that the currents employed were biocompatible. Uninfected H9 cells were
exposed to the same conditions used for the viral aliquots.
There was no significant change in the percentage of viable
uninfected cells exposed to any of the currents tested. Therefore, because biocompatible
direct electric current attenuates the infectivity of cell-free virus, this treatment may
allow development of new strategies to prevent transmission of HIV-1 through either
treating the general blood supply or developing alternative barrier contraceptive devices.
Additionally, biocompatible electric. current may be applicable for the direct treatment
of AIDS patients by utilizing either extracorporeal systems or self contained indwelling
electrodes. Lastly, because the virus is being attenuated, electric current may also
render treated HIV-1 suitable for vaccine development.
Key words: HIV-1, AIDS, treatment, suppression of
infectivity, electricity
INTRODUCTION
The number of individuals infected by the human immunodeficiency
virus type-1 (I-(HIV-1) continues to increase on a world-wide basis (1). A significant
percentage, if not all, of these individuals will eventually develop the acquire d
immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) (2)- While horizontal transmission in the homosexual.
population may be contained or decreasing (3), heterosexual transmission and infection
through contaminated blood supplies continues to increase (4). Additionally ver tical
transmission from infected females to their fetuses is also on the rise with a resultant
increase in the number of children with AIDS (5). New strategies, therefore, must be
devised in order to limit more effectively the spread of this virus.
In this regard, three principal approaches are currently being
investigated. In order to decrease susceptibility to the consequences of infection,
vaccines are being sought which will induce the production of protective antibodies (6).
As treatment modalities, the use of soluble antagonists to block the receptor for HIV-1 is
being studied (7) as are pharmacologic agents such as nucleic acid analogs which can
interfere with the transcription of viral genomic sequences (8). Each of these systems
has------------ and limitations and to date none has proven completely effective.
Because heat or light in combination with drugs and dyes can
inactivate viruses including HIV-2 in vitro (9), others have suggested the use of
these forms of energy to treat .. AIDS patients. The results of studies using heat have
not been peer- reviewed and are therefore impossible to evaluate. The use of light with
drugs ["photopheresis"] (10) appears to be efficacious although this treatment
may be limited by drug toxicity and the potential long-term effects of ultraviolet
radiation on blood c ell nucleic acids. Also, by its nature, this last system may not be
suitable for the treatment of tissue-associated virus.
As result of our interest in the use of electric current to alter
biological systems , we focused our investigations on the ability of direct electrical
current at biocompatible levels to alter the infectivity of HTV-1 for susceptible CD4
positive cell s in vitro.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Electrical treatment of HIV 1:
The RF strain of HIV-I (AIDS Reagent Program) was cryopreserved
prior to treatment at -70°C. Fur treatment, a sample of virus was thawed and maintained
on ice at 4°C . Ten microliters (μl) of HIV-1 at a concentration of 105 infectious
particles per ml were placed into a chamber which included a pair of platinum electrodes
1mm apart permanently mounted into a well 1.56mm in length an d 8.32mm in depth equal to
12.9 μl volume capacity. The chamber was connected to a power supply capable of creating
constant direct current. The viral aliquots were exposed to direct currents ranging from 0
microamperes ( μA) for up to 12 minutes to 100μA for up to 6 minutes. Intermediate
currents of 25, 50 and 75μA were used to expose similar viral aliquots. Under these
conditions, for example, 0, 50 and 100μA represent 0, 3.85 and 7 .7μA/mm2
current densities respectively. The current was monitored throughout the experiment. A
matrix of current and time employed is shown in Table 1.
After the exposure of virus to electric current, the contents of
the chamber were removed and placed into sterile microtubes. Five μl of each sample were
removed and diluted with 95μl tissue culture medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf
serum (FCS) for subsequent assays.
Syncytium-formation assays:
This assay was performed as previously described by Nara et
al (11). Briefly, 105 CEM-SS cells were dispensed into poly-L-lysine
coated microliter wells. Thereafter, tenfold dilutions o f H9 cells incubated with the
treated HIV-1 samples were co-cultured in triplicate for up to 4 days with the CEM-SS
cells. Identical wells were prepared with control uninfected and infected cells. The wells
were examined for syncytium formation at 2 and 3 days and quantified using an inverted
microscope.
RReverse trascriptase assay:
Uninfected H9 cells, were pelleted at 1,000 rpm for minutes at
room temperature, the supernatant was decanted and the cells were resuspended in 100μl
treated viral sample. The cells were incubated for up to 6 hours with the viral samples.
At the end of the incubation time, the viral/cell suspensions were centrifuged at 1,000
RPM for 5 minutes and the supernatant decanted. The cell pellet was then resuspended in
5ml of RPMI, 10% FCS and placed into a T25 tissue culture flask and maintained at 370C,
5% CO2 in a humidified chamber. At 2 day intervals (beginning at day 2}, 1ml of
the cell suspensions was removed from each sample and centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 5
minutes in order to pellet the cells. The supernatant was subsequently centrifuged at
14,000 RPM for I5 minutes. The pellet was resuspended in suspension buffer and assayed
using standard methodology employing Mg+ + as the divalent cation poly (rA) oligo d(T)
12-18 as template primer, and tritiated thymidine (3H-TdR) which comprise the
reaction mixture. Known HIV positive and negative control samples were included in each
assay for reference. Thirty μl of the reacti on mixture were added to each 10 μl viral
sample and incubated at 37 0C for 60 min. Samples were then incubated with 1ml
of cold quench solution on ice for 15 minutes and filtered through a Millipore manifold.
Chimneys were rinsed first with wash solution and followed by cold 95% ethanol. The
filters were dried by vacuum and counted in scintillation fluid. Reverse transcriptase
activity is expressed as counts per minute (cpm) and is considered positive only if cpm
are at least five times greater than the cpm obtained with HIV negative control samples.
Biocompatibility of electric currents/time:
To determine if the electric currents used were in a
biocompatibility range of energy, uninfected H9 cells were exposed to distinct currents
for different amounts of time. The H9 cells were washed two times in Hanks Balance Salt
Solution (HBSS). Thereafter, the cells were resuspended in RPMI, 10% FCS at a
concentration of 106 cells per ml, Ten μl of the cell samples were placed into
the reaction c hamber. The cell samples were then exposed to 0, 50 or 100μA for 0, 3 or 6
minutes. At the end of each test, the cell sample was removed from the chamber and
approximately 10μl of the sample was mixed with 90μl of trypan blue. The number of
viable cells w as determined by trypan blue exclusion using a hemocytometer and tight
microscope. Results are expressed as percentage of viable cells from the total of all
cells. At least 200 cells per field were counted.
Statistical analysis:
Results of the syncytium-formation and reverse transcriptase assays were
tested for statistical significance by the Student's t test and analyses of variance.
RESULTS
Syncytium-formation assay:
Using this index of HIV-1 infectivity, it was determined that
exposing virus to direct electric current suppressed its capacity to induce the formation
of syncytia. Figure 1 shows a representative e xperiment and Table 2 shows the Croup data
for 3 separate experiments. As can be noted in Figure l, a statistically significant
(p<0.001) reduction in sycytium number was observed and this reduction was dependent
upon the current applied to the viral i solate. At three different viral dilutions, there
were analogous results in that a total charge of 200μA x min (25μA for 8 minutes)
reduced the number of syncytia from 50 to 65% while a charge of 300μA x min (50μA for 6
minute s, 75μA for 4 minutes or 100μA for 3 minutes) resulted in 90% reduction.
Reverse transcriptase assays:
The direct electric currents to which HIV-1 was exposed also
reduced reverse transcriptase activity. Five separate experiments were conducted and a
representative experiment is shown in Figure 2 and the ;coup data are included in Table 3.
As can be seen in Figure 2, there was a significant decrease in the amount of reverse
transcriptase activity after exposure of the virus to either 50μA for 3 or 6 minutes. An
equivalent reduction in reverse transcriptase activity was also noted with exposure to,
100μA for 3 minutes and almost ablation of reverse transcriptase activity was seen with
exposure of the viral isolate to 100μA for 6 minutes. The group data (Table 3} show that
after exposure to 50μA for 6 minutes, there was a 44% reduction in activity and treatment
of virus with 100μA for 6 minutes resulted in a 94% reduction. An analysis of variance
indicates that t he decrease in reverse transcriptase activity was statistically
significant (p <0.0001).
Biocompatibility of the electric currents/time:
The results of a viability analysis using trypan blue exclusion
criteria applied to uninfected cells exposed to the different currents and times used far
these studies are shown in Table 4. The viability of H9 cells, after exposure to 100μA
fur either 3 or b minutes, did not show a significant decrease when compared to the 0
Current control. After maximum treatment at 100μA for 6 minutes, cell viability was 93%.
Interestingly, in other preliminary experiments in which HIV-infected H9 cells were used,
the results show that at 100 μA there may have been a significant decrease in the number
of viable cells. That is, while an insta ntaneous pulse of 100 μA did not affect the
viability of infected cells, at 3 and 6 minutes of exposure to 100 μA, a decrease in
viability was noted. This decrease was time dependent in that exposure to 100 μA far 3
min utes resulted in a viability of 83% while 100 μA for 6 minutes resulted in a
viability of 80%. Although these data are provocative, they only represent a preliminary
experiment and require further investigation.
With respect to the possibility that the electric current was
transduced into heat, the calculated rise in temperature within the chamber was determined
to be less than 1°C. In order to verify this, a temperature microprobe was introduced
into the cham ber containing tissue culture medium alone. Results of these studies are
shown in Table S. Similar results were obtained when H9 cell-containing medium was placed
in the reaction chamber. The data indicate that for the currents and times used for these
ex periments, there was no alteration in the temperature of the chamber.
DISCUSSION
The results reported here demonstrate that HIV-1 treated with
direct electric currents from 50 to 100μA has a significantly reduced infectivity for
susceptible cells in vitro. This reduction o f infectivity correlates with
the total electric change passing through the chamber. Although extrapolation of these
data predicts that ablation of HIV infectivity may be possible, and additional preliminary
data support this prediction, the expectation t hat some virions may still escape the
electrical effect cannot be discounted. Nevertheless, the .therapeutic potential of
electric current may reside in its ability to lower the viral titer to subclinical
significance or in its incorporation into a strate gy analogous to that of other therapies
in which repeated cycles of treatment eventually achieve remission or cure.
The data presented in this report are based on both quantitative
and quantal determinations of viral infectivity. Although the syncytium-formation assay
can be used to quantify the number of infectious viral particles, this use with respect to
HI V-1 may be abridged because of the ability of free fusigenic peptide (gp41) to induce
syncytia by itself. Therefore, while syncytia were observed at some dilutions of
electrically-treated virus, this may simply represent the presence of soluble gp41 in th e
tissue culture medium. We believe that the correlation between total charge and reduction
in syncytium number more adequately reflects the ability of direct electric current to
reduce HIV-1 infectivity.
This belief is also supported by the results of the reverse
transcriptase assays.
Although a decrease in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase does not
assure reduced infectiousness of this virus for Susceptible cells; we feel that, taken
together with the syncytium-formation data, the results indicate that significant attenua
tion of HIV-I infectivity is achieved by treatment with direct electric currents.
With respect to the biocompatibility of the electric currents and
total charges reported here, two separate sets of evidence are applicable. The first has
to do with the results showing that, by trypan blue exclusion, no significant cyt
otoxicity was induced in by any total charge tested. The other evidence is obtained from
reports which clearly indicates that the amount of electricity used for these experiments
is significantly below presently used therapeutic electric currents which ar e in the
milliampere range (12-16).
Rather than negative effects, exposure of cells to electric
current may actually have positive consequences for resistance to infection in that
important cellular electrochemical changes correlate with enhancement of specific
enzymatic activities. In particular, a facilitation of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and
ATPase activity has been observed (12,15). Both of these enzymes are associated with the
oxidative capacity of the cell. Specifically, it has been suggested that an elec
trochemical reaction occurs between mitochondrial membrane-bound H+ ATPase and ADP
leading to the formation of ATP. Therefore, exposure of cells to direct electric current
may directly or indirectly increase energy resources within a cell and facil itate cell
metabolism. This, in turn, may actualIy render a cell less susceptible to the effects of
viral infection.
In summary, the data presented here indicate that biocompatible
direct electric current significantly reduces the infectivity of HIV-1. Continuing
investigations are exploring the mechanisms through which this effect is mediated. The in
itial focus of these experiments is centered on the potential role which ionic and
molecular species generated by electrolysis may have on the virus. However, the complete
mechanism by which direct electric current attenuates HIV-1 infectivity is undoubte dly
far re complex than simple electrolysis. Nonetheless. and independent of a complete
understanding of all of the mechanisms involved in the attenuation of HIV-1 infectivity,
the present observations may serve as an initiaI step for the development of new
strategies to treat infection or prevent transmission of HIV-1 through either treat ing
the general blood supply or developing alternative barrier contraceptive devices. It may
also be feasible to treat AIDS patients with direct electric current using either
extracorporeal systems or self contained indwelling electrodes. Lastly, because viral
infectivity is being attenuated, electric current may render treated HIV-1 suitable for
vaccine development.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Thanks go to Mrs. Agnes Geoghan for her excellent secretarial
assistance and to Dr.Gabor, Kemeny for important technical help. Additional thanks go to
Drs. Frank Lilly and Philip Aisen for their constructive criticism of this manuscript.
LEGENDS
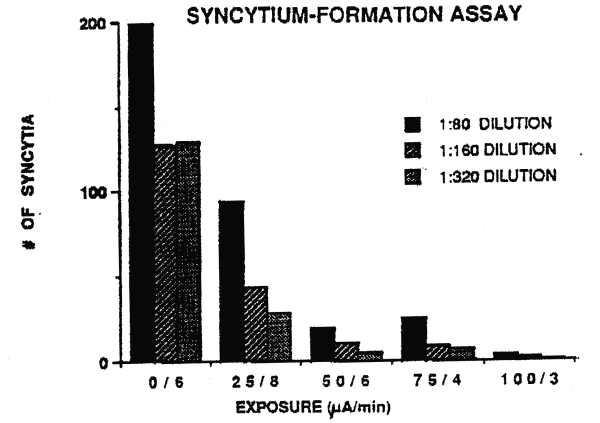
Figure 1. Results of a representative
syncytium-formation assay. Five aliquots of the RF strain of HIV -1 were exposed to
direct electric current for up to 8 minutes. Three of the samples were exposed to a total
electric charge of 300.μA x min (50/6, 75/4 and 100/3). At all the dilutions tested (
shown here), electrical treatment of the virus aliquots resulted in a significant decrease
in syncytium formation. |
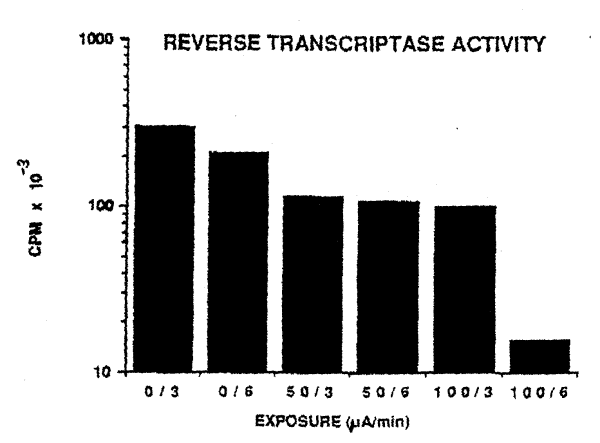
Figure 2. Results
of a representative reverse transcriptase assay. Six aliquots o£ the RF strain of HIIV-1
were exposed to different amounts .of current for 3 or 6 minutes. A. significant decrease
(p < 0. 005)from 0 current levels (0/3 and 0/6) in reverse transcriptase activity is
noted. However, the decrease is more significant (p<0.0001) when virus is exposed to
100μA for 6 minutes. |
Table 1
Experimental Paradigm
Current (μ.A). Time (Minutes)
| 0 |
1 4 8 12 |
| 25 |
2 4 8 12 |
| 50 |
3 4 6 12 |
| 75 |
2 4 8 12 |
| 100 |
1 3 4 12 |
|
Table 2
Effect of ELECTRIC Current on Syncytium Formationa
% of O Current Control (Δ%)b
Current (μA) Six Minute Exposure
| 0 |
100 (0) |
| 50 |
50 (-50) |
| 100 |
35 (-65) |
a = Value at I:160 dilution of virus.
b = Value equals the mean of 3 experiments. |
Table 3
Effect of Electric Current on Reverse
Transcriptase Activitya
% of O Current Control (Δ%)
Current (μa) Six Minute Exposure
| 0 |
100 (0) |
| 50 |
56 (-44) |
| 100 |
6 (-94) |
a = Value equals the mean of 5 experiments.
The standard error of the mean in each case was less than10% of the mean value. |
Table 4
Effect of Eclectic Current onViability of Uninfected H9
Cells
(% Viable CeIIsa)
Length of exposure (Minutes), Current (μA) 0 3 6
| 0 |
96 94 6 |
| 50 |
98 95 98 |
| 100 |
96 97 93 |
a = At feast 200 cells counted in hemocytometer
field |
Table 5
Effect of Electric Current on Temperature of
Tissue Culture Medium a (°C) Length of Exposure (Minutes)
| Current (μA) |
0 3 6 |
| 0 |
19 19 19 |
| 50 |
19 19 19 |
| 100 |
19 19 19 |
a = The temperature was monitored before, during
and after exposure.
Results shown are end-point determinations. |
REFERENCES
1. Sato PA, Chin J, Mann JM. Review of AIDS and HIV infection Giobal epidermiology and
statistics. AIDS 1989; 3 Suppl.1:S301-7.
2. Centers for Disease Control. Revision of the CDC surveillance case definition for
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. MMWR 1987; 1 Suppl. 36:S1-15.
3. Thacker SB, Berkelman RL. Public health surveillance in the United States.
Epidemiol. Rev 1988; 10:164.90.
4. Klein RS, Friedland GH. Transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type (HIV-1) by
exposure to blood: Defining the risk. Ann Int Med 1990; 113:729-30.
5. Oxtoby MJ. Epidemiology of pediatric AIDS in the United States. In: Brain in
Pediatric AIDS (Kozlowski PB, Snider DA, Vietze PM, Wisniewski HM, eds) 1990:1-8
6. Broder S, Mitsuya H, Yarchoan R, Pavlakis GN. Antiretroviral therapy in AIDS. Ann
Int Med 1990: 113:604-18.
7. Perno CF, Baseler MW, Broder S, Yarchoan R. Infection of monocytes by human
immunodeficiency virus I blocked by inhibitors of CD4-gp120 binding, even in the presence
of enhancing antibodies. J Exp Med 1990; I71:1043-56.
8. Mitsuya H, Weinhold KJ, Furman FA et al. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): an
antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human
T-lymphotropic virus type III/ lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA 1985; 82:7096-100.
9. Quinnan GV, Wells MA, Wittek AE, et al. Inactivation of human T-cell virus, type III
by heat, chemicals and irradiation. Transfusion 1986; 26:481-3.
10. Bisaccia E, Berger C, KIainer AS. Extracorporeal photopheresis in the treatment of
AIDS-related complex: A pilot study. Ann Int Med 1990; 113:270-75.
11. Nara PL, Hatch WC, Dunlop NM, et al.: Simple, rapid quantitative, syncytium-forming
microassay for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibody. Aids
Res Hum Retrovirus 1987; 3:283-302
12. Cheng N, Van Hoof H, Bockx E, et al. The effects of electric currents on ATP
generation, protein synthesis, and membrane transport in rat skin. Clin Ortho ReI Res
1982; 17I:26472.
13. Frank G, Schachar N, Dittrich D, et al. Electromagnetic stimulation of ligament
healing in rabbits. Clin Ortho ReI Res 1983; I75:263-72.
14. Eriksson E, Haggmark T. Comparison of isometric muscle training and electrical
stimulation supplementing isometric muscle training in the recovery after major knee
ligament surgery. Amer J Sports Med 19?9; 7:159-71.
15. Stanish WD, Valiant GA, Bonen A, et al. The effects of immobilization and of
electrical stimulation on muscle glycogen and myofibrillar ATPase. Can J Appl Sport Sci
1982; 7:267-71.'
16. Pills AA. Electrochemical information transfer at living cell membranes. Ann NY
Acad Sci 1974; 205:148-70.
================================================================================
VIDEO
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l_z9FQxfeT0
IS
NO LONGER AVAILABLE IN
"YOU
TUBE"
.....CLICKHERE
For the saved page from
youtube
CLICKHERE
For the saved page's title from google
CLICKHERE
SOME STATISTICAL DATA FOR THIS VIDEO EXIST IN
"YOU TOMB" : http://youtomb.mit.edu/youtube/l_z9FQxfeT0
clickhere
CLICK HERE
FOR THE SAVED WEBPAGE FROM "YOU
TOMB"
Below follow three ''YOU TUBE" videos with the same theme
........

================================================================================
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XAXCwFJVeuA
v=XAXCwFJVeuA for the saved webpage click here
http://www.youtube.com/comment_servlet?all_comments&v=XAXCwFJVeuA&fromurl=/watch%3Fv%3DXAXCwFJVeuA
saved webpage with
All Comments (162 total)
================================================================================
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V1otPs4slq0
v=V1otPs4slq0 for
the saved webpage click here
http://www.youtube.com/comment_servlet?all_comments&v=V1otPs4slq0&fromurl=/watch%3Fv%3DV1otPs4slq0
saved webpage with
All Comments (239 total)
click here
================================================================================
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kZ4nOCJsbQo
v=V1otPs4slq0
for the saved webpage click here
http://www.youtube.com/comment_servlet?all_comments&v=kZ4nOCJsbQo&fromurl=/watch%3Fv%3DkZ4nOCJsbQo%26feature%3Drelated
saved webpage with All Comments ( 37 total)
click here
================================================================================
see also :
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-234247273689402090&hl=en
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=2095786730805958061&hl=en
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-3383948315844437935&hl=en
================================================================================
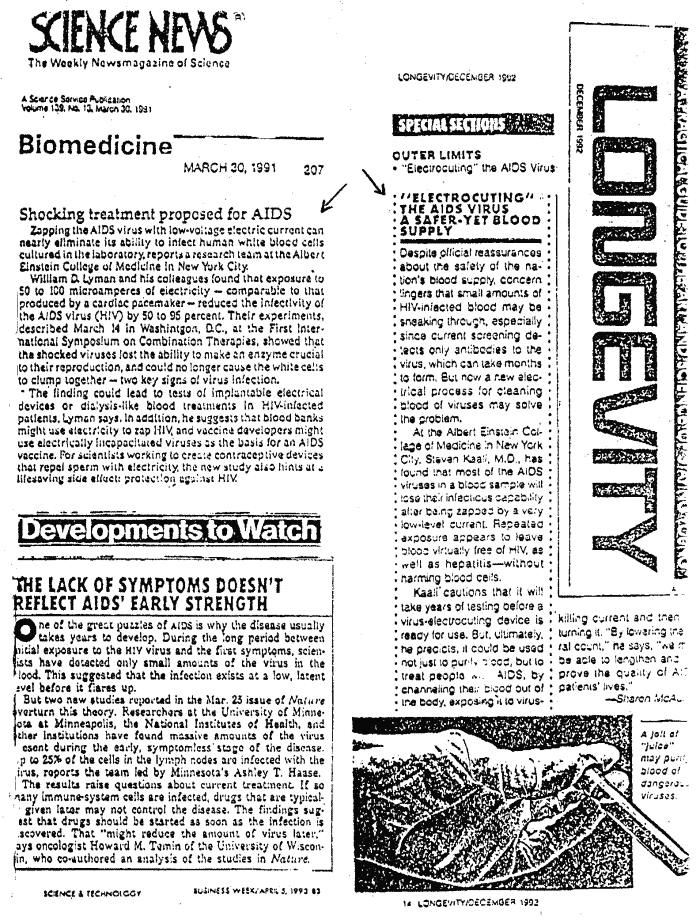
|



